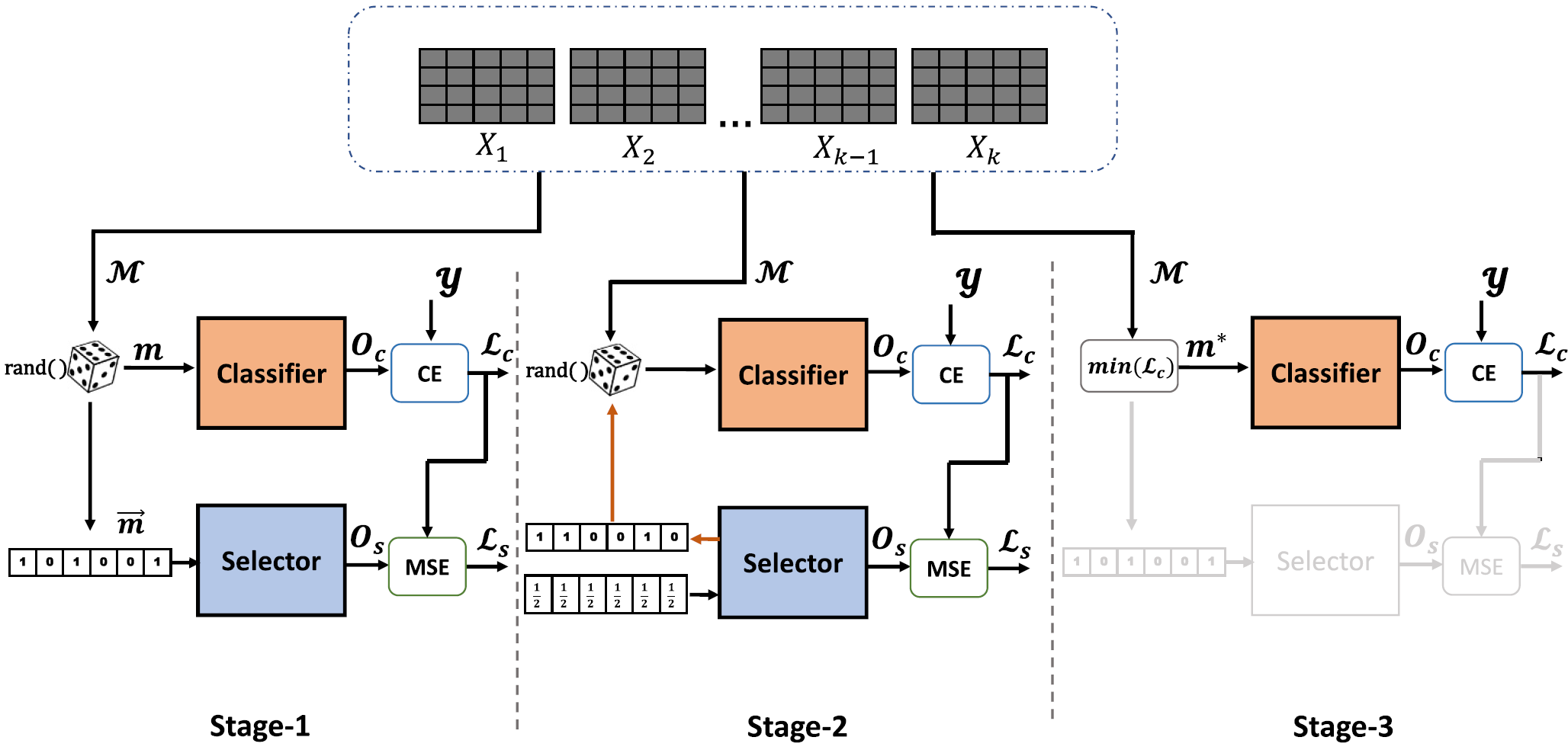
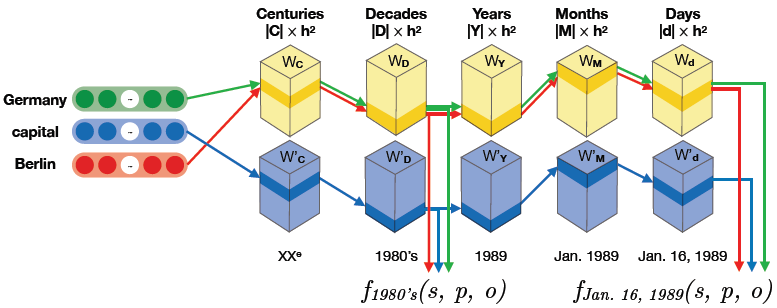
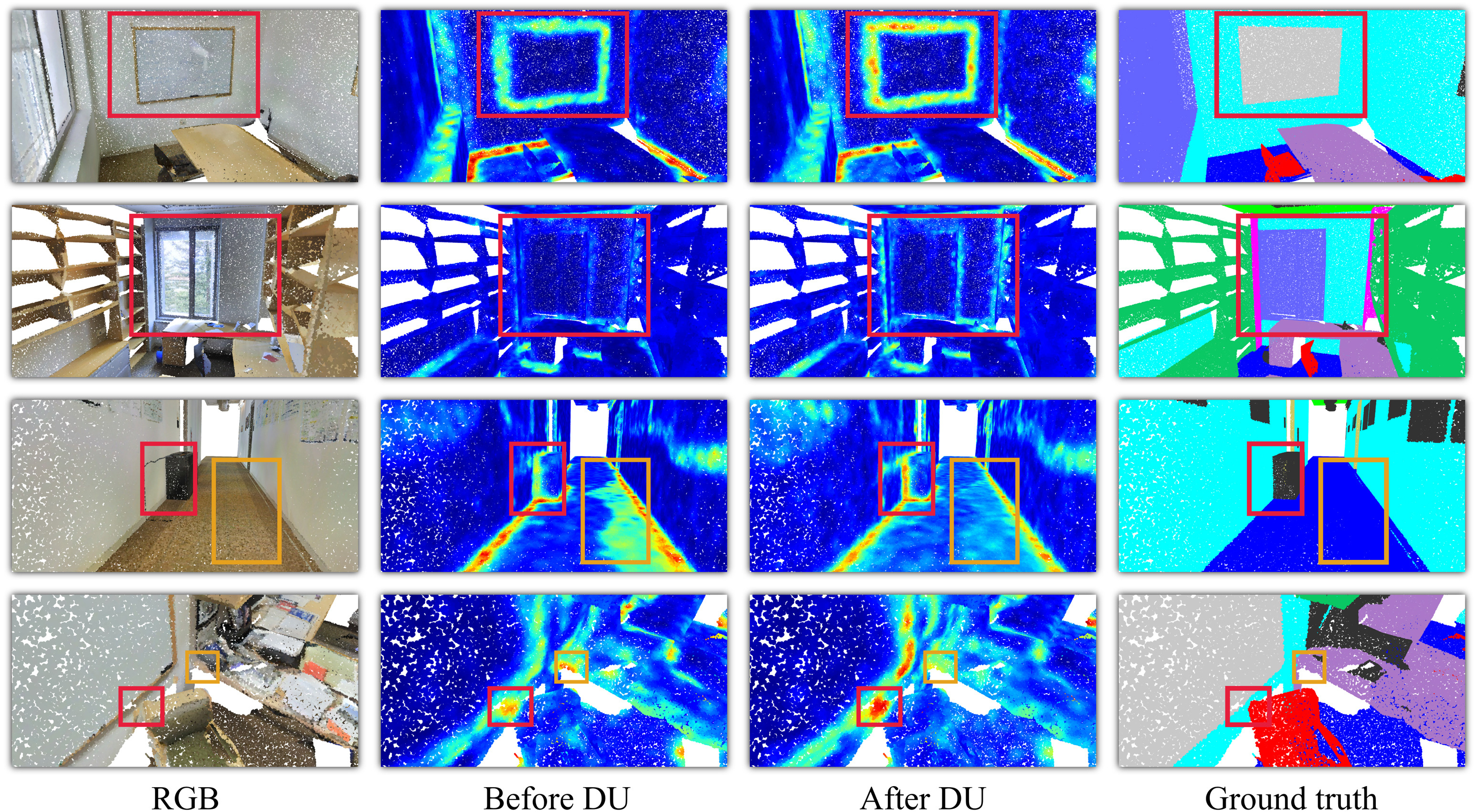
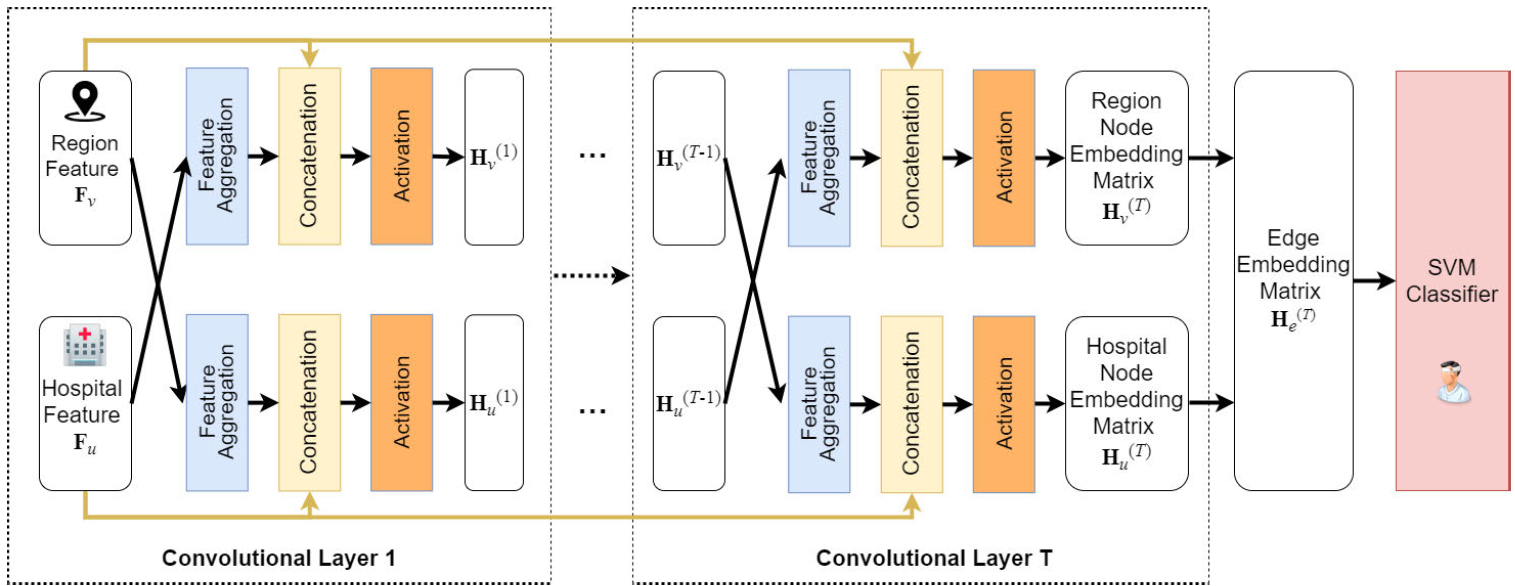
Graph convolutional networks for graphs containing missing features
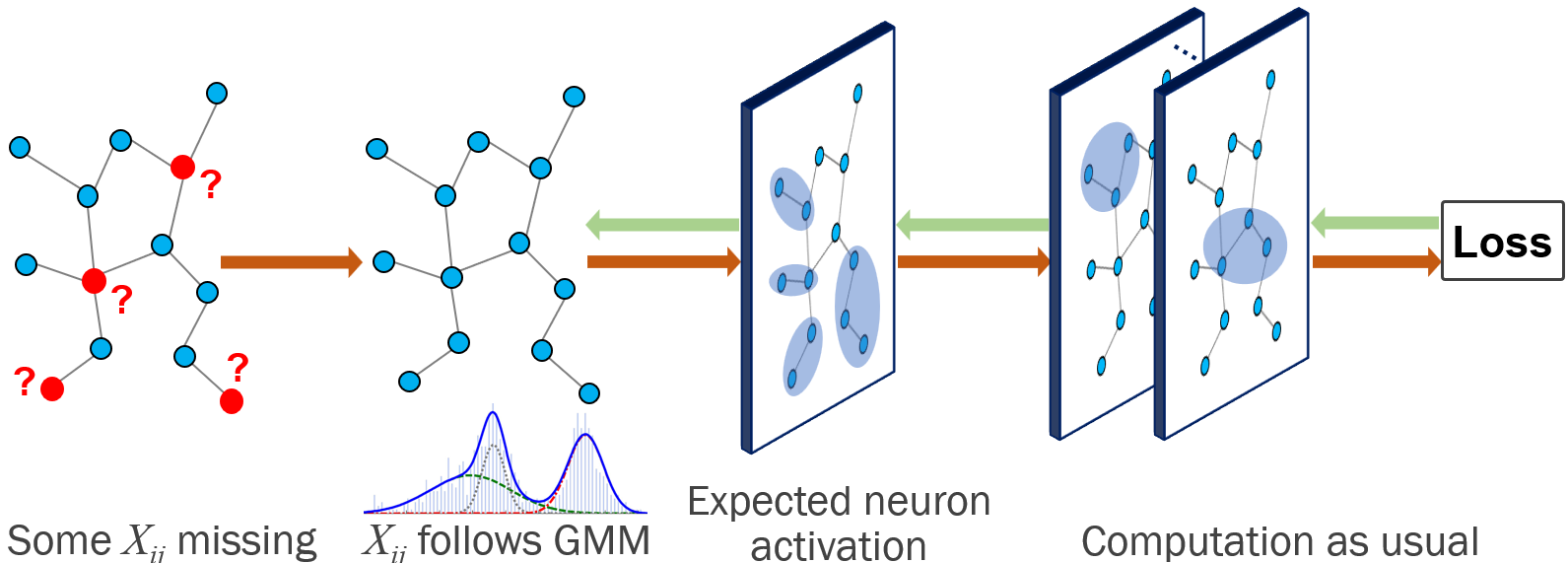
GCN variant that handles missing features by modeling them with a GMM and computing expected activations in the first hidden layer
Future Generation Computer Systems, vol.117, pp.155-168, 2021